HPV and Anal Cancer: What’s the Connection?
Anal cancer, though relatively rare, is becoming a growing concern—particularly due to its association with Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Many people ask, “Can HPV cause anal cancer?” The answer is yes.
In fact, the majority of anal cancer cases are directly linked to persistent HPV infections.
Let’s explore how HPV contributes to the development of anal cancer, its symptoms, causes, and the best treatment options available in Dombivli.
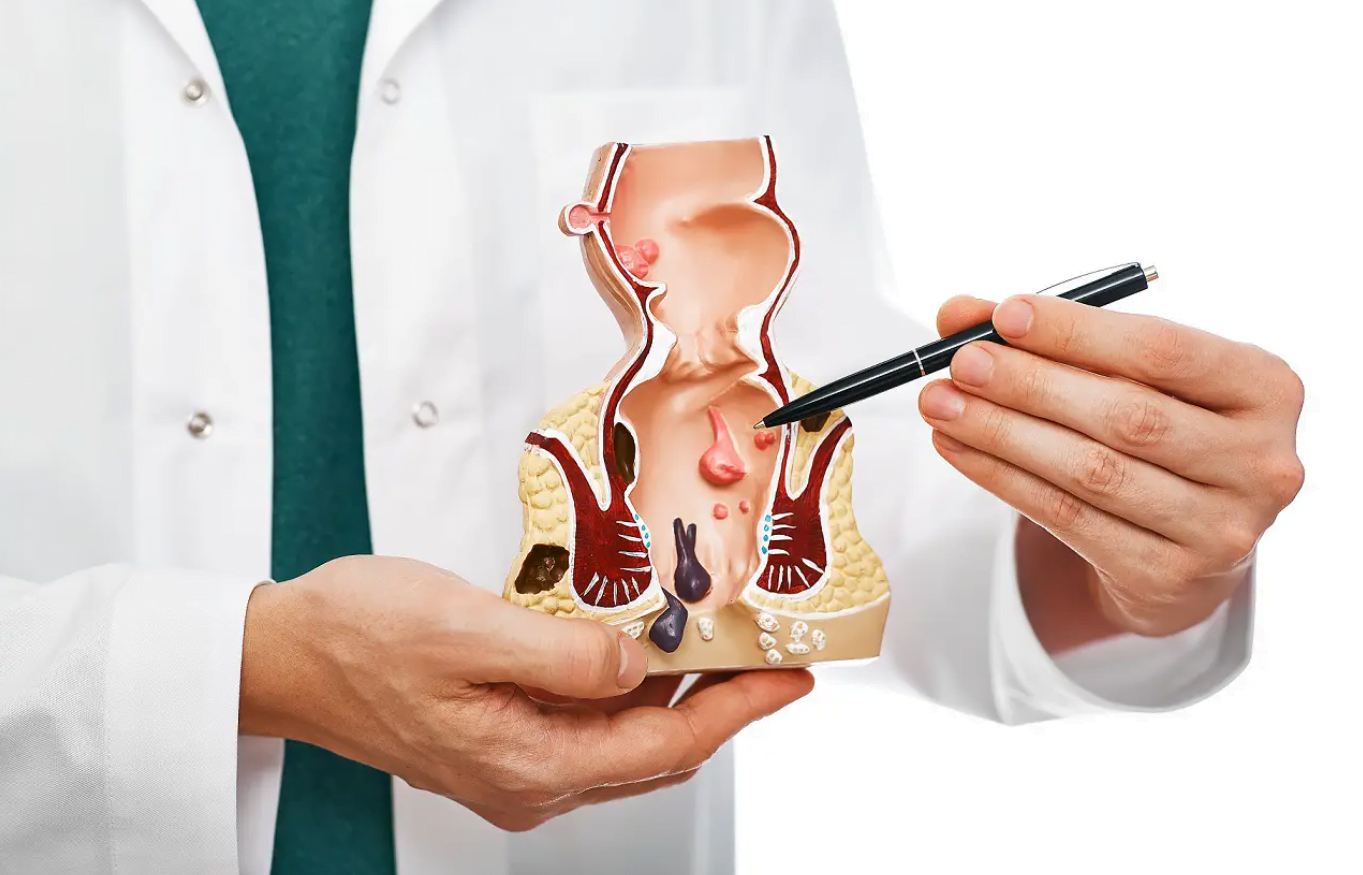
What is Anal Cancer?
Anal cancer is a condition where malignant cells form in the tissues of the anus—the opening at the end of the rectum.
It is different from colorectal cancer and often linked to viral infections, especially HPV.
- It may start in different cell types, with squamous cell carcinoma being the most common.
- Though rare, its incidence is rising, especially among people with compromised immune systems.
Early diagnosis and treatment by an experienced specialist like Dr. Pramod D. Bahekar, a reputed Anal Cancer Surgeon in Dombivli East with 37+ years of experience, can greatly improve outcomes.
He consults at Amrut Hospital Dombivli, a trusted center for specialized care in the region.
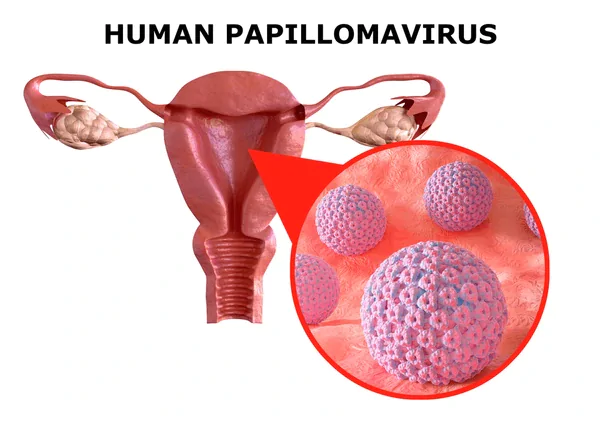
What is HPV Cancer?
HPV cancer refers to cancers caused by the Human Papillomavirus, a group of more than 150 related viruses. Certain types of HPV are considered high-risk and have been linked to cancers of the:
- Cervix
- Throat
- Penis
- Vagina
- Vulva
- Anus
What is HPV Cancer? It’s essentially a cancer that develops when persistent HPV infection causes cell mutations, leading to uncontrolled growth and malignancy.
Can HPV Cause Anal Cancer?
The Direct Link Between HPV and Anal Cancer
Yes, HPV can cause anal cancer. Studies show that over 90% of anal cancer cases are associated with high-risk HPV strains, especially HPV-16 and HPV-18. These strains damage the DNA of anal cells, leading to mutations that result in cancer.
Risk Factors for HPV-Related Anal Cancer
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Receptive anal intercourse
- Smoking
- A weakened immune system (HIV/AIDS)
- History of genital warts or other HPV-related diseases
Anal Cancer Causes and Risk Factors
Anal Cancer Causes Explained
While HPV infection remains the leading cause, other factors can also contribute:
- Chronic inflammation in the anal area
- Precancerous conditions like AIN (anal intraepithelial neoplasia)
- Smoking
- Genetic predisposition
Non-HPV Related Causes of Anal Cancer
- Long-term untreated anal fistulas or abscesses
- History of radiation therapy in the pelvic area
- Chronic immunosuppression due to medication or disease
Recognizing the Symptoms
HPV Anus Cancer Symptoms to Watch For
- Unexplained anal bleeding
- Persistent itching or pain
- Lumps or masses in the anal canal
- Discharge or swelling in the anal region
- Bowel movement changes
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin
These HPV anus cancer symptoms can be subtle initially.
If you notice any, consult a trusted specialist like Dr. Pramod D. Bahekar for a prompt evaluation at Amrut Hospital Dombivli, known for its patient-focused oncology care.
Importance of Early Screening
People at high risk should consider:
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
- Anal Pap Smears
- High-resolution anoscopy
- HPV DNA testing
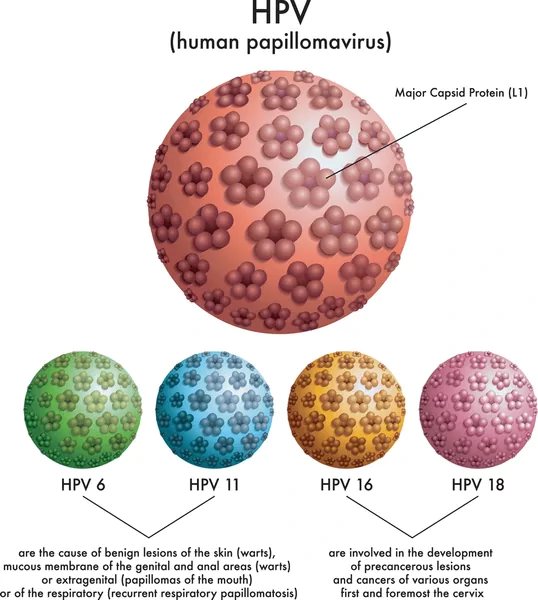
Human Papillomavirus Types and Their Impact
High-Risk HPV Strains
- HPV-16 and HPV-18 are the most cancer-causing types.
- Responsible for nearly all HPV-related anal and cervical cancers.
Low-Risk HPV Strains
- Types like HPV-6 and HPV-11 cause genital warts.
- Rarely lead to cancer but can signal HPV presence and future risks.
Understanding the Human papillomavirus types can help in targeted screening and prevention.
How Anal Cancer is Diagnosed?
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
- Anoscopy or Proctoscopy
- Biopsy of any abnormal growths
- Imaging tests like MRI, CT scan, or PET scan to detect cancer spread
Anal Cancer Treatment in Dombivli
Under the care of Dr. Pramod D. Bahekar, patients receive:
- Comprehensive diagnosis and staging
- Personalized treatment plans
Treatment options include:
- Surgery: For small, localized tumors
- Radiation therapy: Often combined with chemotherapy
- Chemoradiation: First-line treatment for many cases
As a leading Anal Cancer Surgeon in Dombivli East, Dr. Bahekar ensures patients have access to cost-effective and high-quality treatment at Amrut Hospital Dombivli—a center trusted for specialized cancer care.
Prevention and Awareness
Can Anal Cancer Be Prevented?
Yes! Prevention focuses on:
- HPV vaccination
- Safe sexual practices
- Routine screenings for high-risk individuals
- Quitting smoking
HPV Vaccination and Its Role
- The vaccine protects against major high-risk HPV types
- Recommended for both boys and girls from age 9 to 26
- Also beneficial for adults up to age 45 in certain cases
When to See an Anal Cancer Specialist?
Don’t Ignore These Warning Signs
If you experience:
- Blood during bowel movements
- Anal pain or itching
- Growth or swelling around the anus
…it’s time to see an expert.

Why Choose Dr. Pramod D. Bahekar?
- Highly experienced Anal Cancer Surgeon in Dombivli East
- 37+ years of clinical excellence
- Offers cost-effective anal cancer treatment in Dombivli
- Uses the latest diagnostic and treatment protocols
- Compassionate, patient-centered care at Amrut Hospital Dombivli
FAQs
Q1. Can HPV cause anal cancer in men and women?
Yes. Both men and women are at risk of HPV-related anal cancer, especially those engaging in receptive anal intercourse or with compromised immune systems.
Q2. How is anal cancer different from colon or rectal cancer?
While they share some symptoms, anal cancer begins at the anal opening, whereas colon and rectal cancers start deeper in the large intestine.
Q3. What are the early signs of anal cancer?
Early signs include anal bleeding, itching, pain, and lumps. However, some individuals may remain symptom-free until the disease progresses.
Q4. Is HPV always sexually transmitted?
Most HPV types are sexually transmitted, but skin-to-skin contact in the genital area can also spread the virus.
Q5. Can the HPV vaccine prevent anal cancer?
Yes, vaccines like Gardasil protect against high-risk HPV types, significantly lowering the risk of anal and other HPV-related cancers.
Conclusion
HPV is a major contributor to anal cancer, but the good news is that it’s preventable and treatable—especially when detected early. Stay informed, practice preventive care, and if you notice any symptoms, don’t delay.
Dr. Pramod D. Bahekar, a trusted Anal Cancer Surgeon in Dombivli East with 37+ years of experience, provides cost-effective and comprehensive treatment at Amrut Hospital Dombivli.
Book your consultation today and take control of your health.
